Glutamine is arguably the most mysterious and practical supplement. Athletes use it to increase strength, accelerate recovery and improve health in general. The effects of intake often exceed expectations. Muscle mass starts to grow faster, the energy required for productive training appears, the immune system starts to work more productive, etc. Any possible effects will manifest themselves noticeably after several months of regular intake.
What is Glutamine
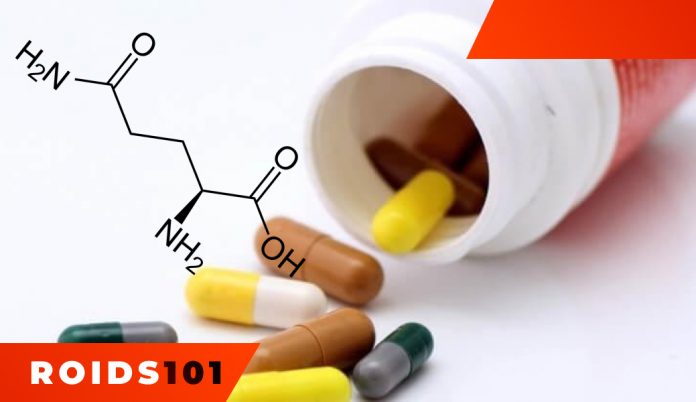
Glutamine is one of the twenty amino acids which form a protein cell and amounts for 60% of its total composition. This fact alone indicates the necessity of this substance not only for professional athletes but for ordinary people as well. The supplement comes in the form of capsules, tablets, and loose powder.

If you intend to take it, you should clearly understand its effects on the body, what to expect, the correct dosage, and intake regimen.
Effects Of Glutamine
The action of glutamine is rather diverse:
- it bounds harmful ammonia, which is a by-product of specific reactions and accumulates in the body due to malnutrition. Glutamine reduces the impact of this toxic substance on the brain, thus increasing mental functions;
- it dramatically reduces fat deposition on the liver, thus protecting the primary «filter» of the body;
- it disposes of metabolic products that remain after the breakdown of fats. Such a powerful cleanup effect is useful for absolutely all body systems;
- it strengthens the immunity, which is especially vulnerable under hard training stress. As general experience shows, athletes taking glutamine are much less prone to colds and other diseases of similar nature;
- it catalyzes protein synthesis processes, which subsequently leads to more active muscle growth;
- it suppresses cortisol or stress hormone, reducing its harmful effects on the body;
- it increases the production and activity of growth hormone (GH). Most often, this specific effect in the reason why professional athletes are attracted to the supplements;
- it improves the quality of metabolic processes. It results in much better absorption of useful substances from foods and supplements and their further utilization;
- blood flow to the brain is normalized, which significantly improves mental capabilities; it normalizes blood supply to the brain, which enhances mental capabilities significantly;
- It strengthens bone tissue, which reduces the risk of injury during a workout.
So, it’s quite evident that glutamine is a wonderful supplement, and for many athletes, the choice of whether to take it or not is obvious.

Dosage And Intake Features
Like with any supplement, the correct dosage plays an important part. Glutamine is no exception. According to manufacturers and practicing athletes, the optimum is 10-30 grams daily. The more precise individual dose is calculated through multiplying body weight by 0.3. For example, if your body weight is 80 kilos, your daily dose is 80 * 0.3 = 24 grams.
Another useful hint is that the entire daily dose should be divided into several parts and taken by portions. Here are some regimens:
- The daily portion is divided into two. One part is taken before a workout (30-40 minutes before it), the other – right after a workout (20-30 minutes).
- The daily portion is divided into two. One part is taken in the morning, the other – before bedtime.
- The daily dose is divided into four. Two of these portions are taken as in the first regimen, while the other two – like in the second regimen. Experienced bodybuilders claim this option of intake to be the most effective.
Bear in mind that glutamine is supposed to be taken on an empty stomach. This way, it gets properly absorbed and produces the maximum effect. Moreover, it is supposed to be ingested right after dilution (if you take it in the form of powder).
Conclusion
It is necessary to follow recommendations on the correct dosage and intake regimen of glutamine to make the most of this supplement.